As a result, there will be no need for you to manually enter or upload all your invoices, and your purchase and payment process would also get automated. It’s essential that you to review your supplier contracts on a regular basis as it helps to prevent fraudulent billing practices, whether due to overpayment or duplicate payments. Let’s consider the above example again to understand how to record accounts receivable. Accounts payable typically cover a range of short-term debts from purchases of goods and services.

Process Payment
Accounts payable most commonly operates as a credit balance because it is money owed to suppliers. However, it can also operate as a debit once the money is paid to the vendor. An aging schedule separates accounts payable balances, based on the number of days since the invoice was issued. Acme Manufacturing, for example, has $100,000 in payables from 0 to 30 days old, and $15,000 due in the 31-to-60-days-old category. Timely and accurate payments help maintain strong relationships with your suppliers. Automation ensures that invoices are processed and paid promptly, reducing the risk of late fees and fostering trust with your vendors.
Accounts payable vs accounts receivable
Keeping a close eye on accounts receivable helps you ensure timely payments from customers, which is vital for maintaining a healthy cash flow. Accounts payable and its management is important for the efficient functioning of your business. As a result, the suppliers would provide goods or services without any interruption.
- Accounts payable is a kind of short-term debt to be settled from somewhere ranging from a week to a month after receiving the invoice.
- Accounts payable are a type of account that records money you owe to others in the short-term.
- You need to make your accounts payable process efficient so that it provides a competitive advantage to your business.
- When you make a payment on a loan or settle a bill, you debit the account, which reduces what you owe.
- Accounts payable represents money owed in the form of short-term debt.
Journal entries related to accounts payable
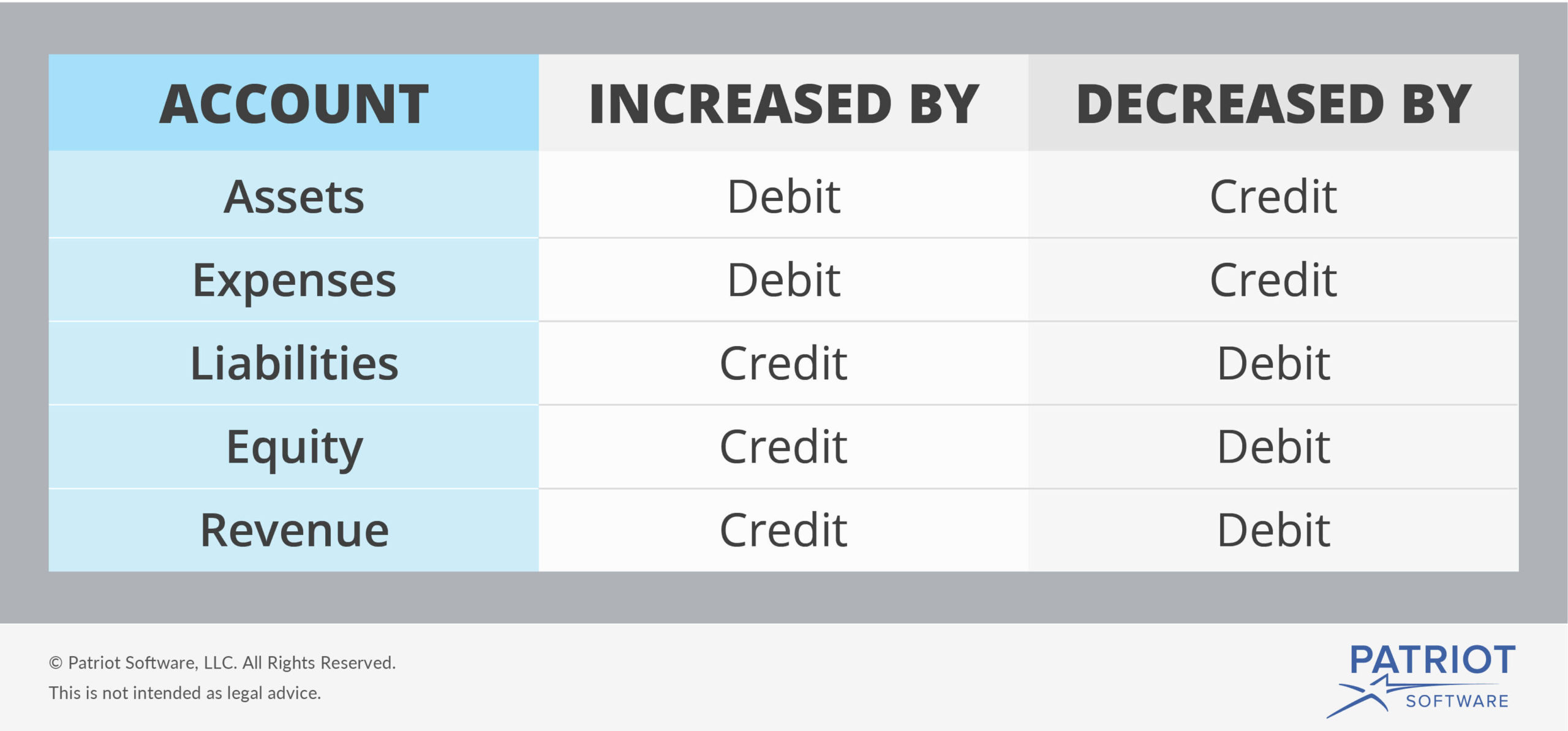
When you place an amount on the normal balance side, you are increasing the account. If you put an amount on the opposite side, you are decreasing that account. Debits and credits are a critical part of double-entry bookkeeping. They are entries in a business’s general ledger recording all the money that flows into and out of your business, or that flows between your business’s different accounts. After recording above journal entry, the buyer sends a debit note (also known as debit memo) to the seller to inform him that his account has been debited for the value of goods returned.
With automated accounts payable, you gain real-time insights into your financial status. You can easily track pending invoices, payment statuses, and overall cash flow, allowing you to make informed decisions quickly. Business owners must monitor the accounts payable balance and use a cash forecast to plan the payments. A company’s cash position is important because every firm needs a minimum cash balance to operate. Owners must consider the timing of cash inflows from accounts receivable and the cash outflows required for accounts payable.
Analysis of Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio Formula
The debit offset for this entry generally goes to an expense account for the good or service that was purchased on credit. The debit could also be to an asset account if the item purchased was a capitalizable how to become xero certified asset. When the bill is paid, the accountant debits accounts payable to decrease the liability balance. The offsetting credit is made to the cash account, which also decreases the cash balance.
As explained earlier, not all the money owed by a company to creditors is eligible for AP entry. While it might seem like debits and credits are reversed in banking, they are used the same way—at least from the bank’s perspective. Here are some examples to help illustrate how debits and credits work for a small business. Within each, you can have multiple accounts (like Petty Cash, Accounts Receivable, and Inventory within Assets).
Since the financial crisis, trade credit in the form of accounts payable and accounts receivable has become a stable source of funding. Loans payable is an account that records the amount of money you’ve lent from another party. Your loans payable account shows up as a liability on your company’s balance sheet. A trial balance is a worksheet where all the ledgers are compiled into debit and credit column totals.
When a business receives goods or services, the accounts payable increases by recording a credit to this account. Once the payable amount is paid, the accounts payable balance decreases by recording a debit.. In financial and accounting terms, a liability refers to something a person or company owes, typically a sum of money. In the context of a business, liabilities are an essential part of the balance sheet and are categorized into current and long-term. Accounts payable refers to the amount owed by a business to its creditors or suppliers.
