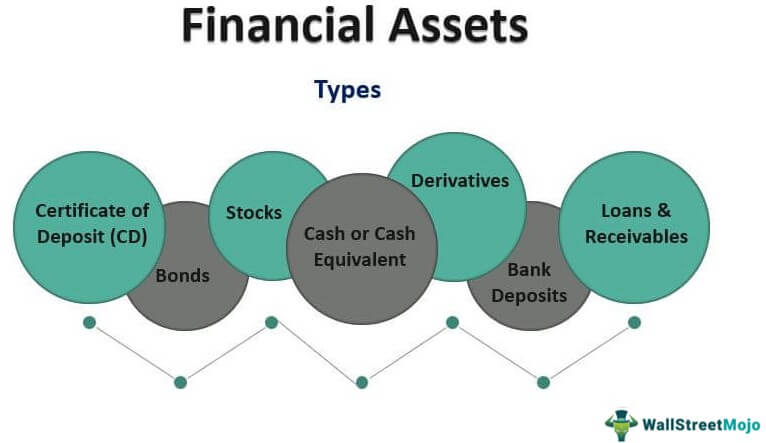
The customer (Company) keeps a set amount of money deposited in the bank for the agreed term in exchange for a guaranteed interest rate. Financial assets may seem intangible—non-physical—with only the stated value on a piece of paper such as a dollar bill or a listing on a computer screen. What that paper or listing represents, though, is a claim of ownership of an entity, like a public company, or contractual rights to payments—say, the interest income from a bond. Financial assets derive their value from a contractual claim on an underlying asset.
Speculative, Equities-Focused Portfolio
They can be easily converted into cash and traded in the financial markets. Understanding financial assets is essential for making informed investment decisions. Cash and cash equivalents include any savings deposits, certificates of deposit (CDs), money market deposit accounts, and money market funds. These assets are considered safe, strong investments by the federal government. A CD, for example, is a type of savings account offered by banks and credit unions that typically earns interest at a fixed rate.
Foreign Exchange Instruments
- Personal assets include such things as your home, artwork you might own, your checking account, and your investments.
- They can be easily converted into cash and traded in the financial markets.
- To fully understand how financial assets work, it’s best to explain the types of financial assets in detail, as each one functions differently.
- An underlying asset can be anything from a commodity to a piece of real estate.
- Because of these changes, in October 2010 the Board restructured IFRS 9 and its Basis for Conclusions.
For instance, it’s typically easier to integrate family income benefit to term life insurance. Many people rely on stocks, bonds and mutual funds for savings and investments. Financial assets are considered liquid, as people can typically sell them easily. But they can also lose value over time, such as during a decline in a company’s share price.
Types of Portfolios
A family term rider allows for the inclusion of spouses or children within the same policy, offering them death benefits under the terms of the primary insured’s policy. A family income policy or a policy with a family income rider pays a specified monthly income to beneficiaries, rather than a lump sum. These options provide ongoing financial support, similar to regular income, ensuring stability after the policyholder’s passing. For example, a conservative investor might favor a portfolio with large-cap value stocks, broad-based market index funds, investment-grade bonds, and a position in liquid, high-grade cash equivalents.
They may be owned by you, like a sofa or your computer, or owed to you, like the $50 you loaned a friend. The loan or borrowed money is considered an asset for you since your friend will repay it to you. Generally, the word may be used to refer to anything of value — from a great work ethic to a great group of friends. But when you’re talking about finances, the term asset is typically used to refer to things that have economic value to a person, a company, and/or a government.
Using the Standards
This provides a financial cushion in the event of an emergency or pressing financial needs. Assets that are less liquid such as real estate require a longer time frame for funds to become available. Liquid assets like checking and savings accounts have a limited return on investment (ROI) capability. ROI is the profit you receive from an asset divided by the cost of owning that asset.
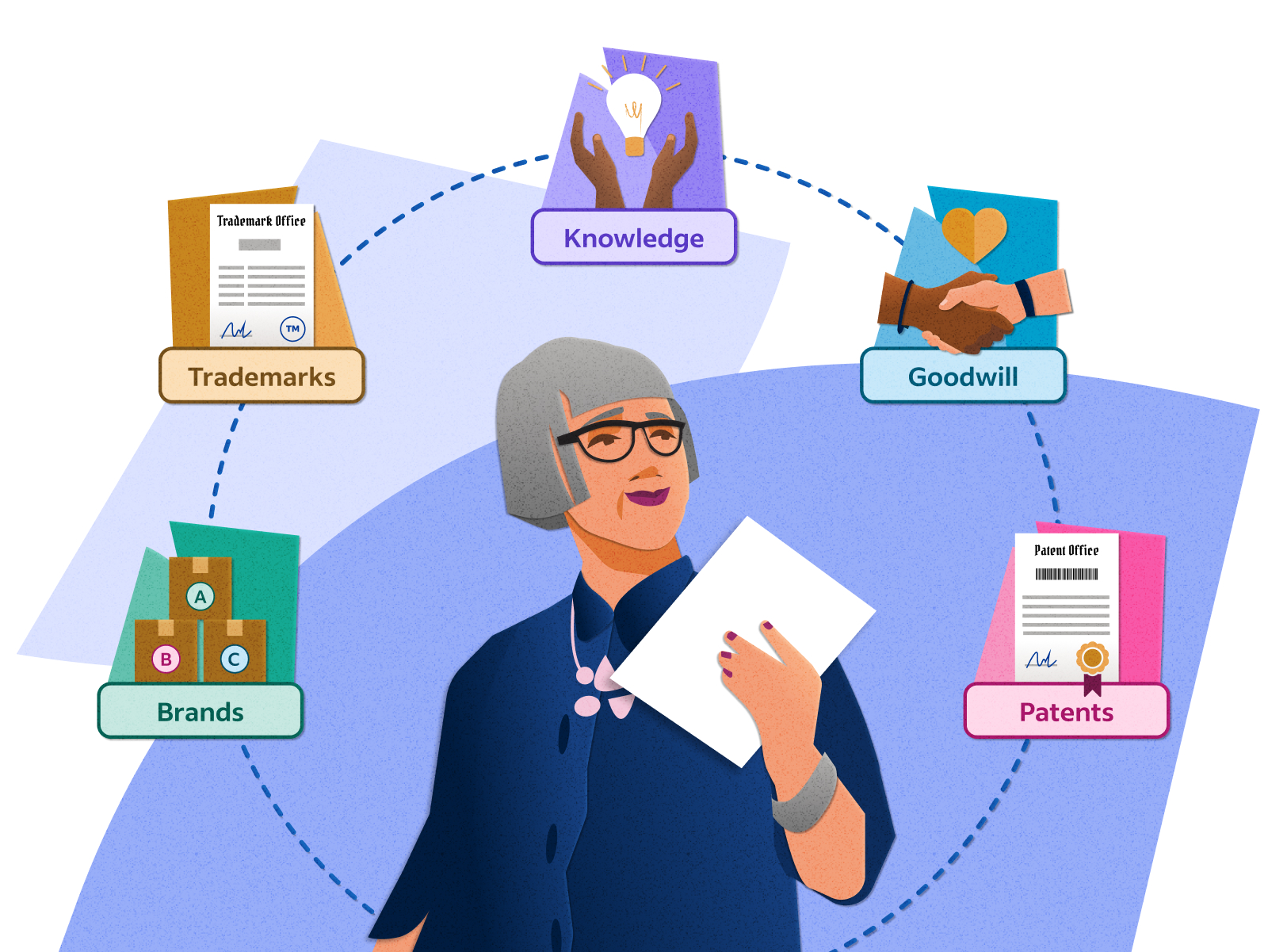
If you can expect to find a number of interested buyers who will pay a fair price, and you can make the sale with some speed, your asset is probably liquid. However, It’s important to do your homework and consider the risks involved since automated platforms are not fully customized to each individual’s specific needs. You also need to be comfortable with the types of investments they may offer, such as ETFs, and make sure you understand the risks and possible costs involved. For example, such things as brand value, reputation, and a company’s customer base are considered goodwill. These intangibles could be highly valued and the reason why a purchasing company might pay more for the company they are buying. An asset can be anything that provides a current or potential future economic benefit to whoever possesses or controls that asset.
Investors should not place undue reliance on forward-looking information as a prediction of actual results. The forward-looking information reflects management’s current expectations and beliefs regarding future events and operating performance and is based on information tips for claiming job currently available to management. Additionally, the Company undertakes no obligation to comment on analyses, expectations or statements made by third parties in respect of Altus Group, the Company’s financial or operating results, or the Company’s securities.
A financial instrument is any document, real or virtual, that confers a financial obligation or right to the holder. ✝ To check the rates and terms you may qualify for, SoFi conducts a soft credit pull that will not affect your credit score. However, if you choose a product and continue your application, we will request your full credit report from one or more consumer reporting agencies, which is considered a hard credit pull and may affect your credit.
Profit (loss) from continuing operations benefitted from higher revenues, offset by higher employee compensation costs, acquisition and related costs and the restructuring program. Fitzpatrick earned a master’s degree in economics and international relations from Johns Hopkins University and a bachelor’s degree from Boston College. He is passionate about using his knowledge of economics and insurance to bring transparency around financial topics and help others feel confident in their money moves. Mark Fitzpatrick is a Licensed Property and Casualty Insurance Producer and MoneyGeek’s Head of Insurance. He has analyzed the insurance market for over five years, conducting original research and creating personalized content for every kind of buyer. He has been quoted in several insurance-related publications, including CNBC, NBC News and Mashable.
